 | SpaceWalker enables interactive gradient exploration for spatial transcriptomics data |  |
Cell Reports Methods - 2023
Download the publication :
![2023_spacewalker.pdf [14.8Mo]](/Publications-new/images/pdf.png)
Motivation
Spatial transcriptomics (ST) enables profiling of the expression of hundreds of genes in tissue sections down to the level of single cells in their tissue environment. The gradient structure of ST data is particularly interesting for tissue biology because spatial gene expression gradients often represent tissue compartment edges, whereas in the single-cell transcriptomic domain, gene expression gradients may represent cell-type differences and smooth phenotypic transitions. Various computational approaches have been developed to extract information from either the spatial domain or the gene expression domain individually. However, integrative biological interpretation of expression gradients in single-cell and ST data spaces remains challenging. Many prior ST analysis pipelines are script based, lack interactive exploration facilities, and do not have specific facilities for automatic identification of localized expression gradients.
Summary
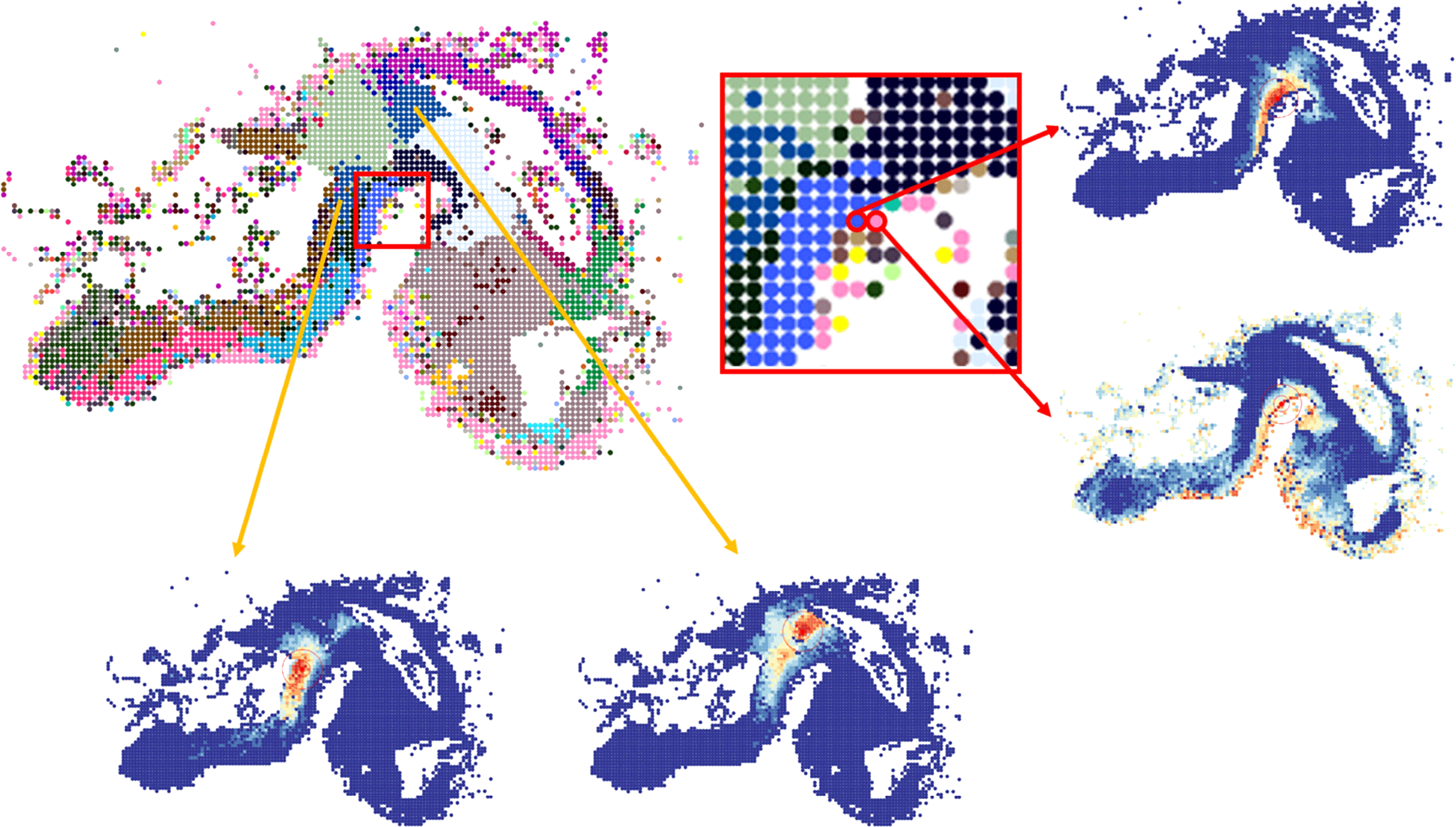
In spatial transcriptomics (ST) data, biologically relevant features such as tissue compartments or cell-state transitions are reflected by gene expression gradients. Here, we present SpaceWalker, a visual analytics tool for exploring the local gradient structure of 2D and 3D ST data. The user can be guided by the local intrinsic dimensionality of the high-dimensional data to define seed locations, from which a flood-fill algorithm identifies transcriptomically similar cells on the fly, based on the high-dimensional data topology. In several use cases, we demonstrate that the spatial projection of these flooded cells highlights tissue architectural features and that interactive retrieval of gene expression gradients in the spatial and transcriptomic domains confirms known biology. We also show that SpaceWalker generalizes to several different ST protocols and scales well to large, multi-slice, 3D whole-brain ST data while maintaining real-time interaction performance.
Images and movies
|
| Other publications in the database
|
BibTex references
@Article { LTKDAHL23,
author = "Li, Chang and Thijssen, Julian and Kroes, Thomas and de Boer, Mitchell and Abdelaal, Tamim and H\öllt,
Thomas and Lelieveldt, Boudewijn P.F.",
title = "SpaceWalker enables interactive gradient exploration for spatial transcriptomics data",
journal = "Cell Reports Methods",
year = "2023",
doi = "10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100645",
url = "http://graphics.tudelft.nl/Publications-new/2023/LTKDAHL23"
}
Back


![2023_spacewalker.pdf [14.8Mo]](/Publications-new/images/pdf.png)

