 | Spectral Gradient Sampling for Path Tracing |  |
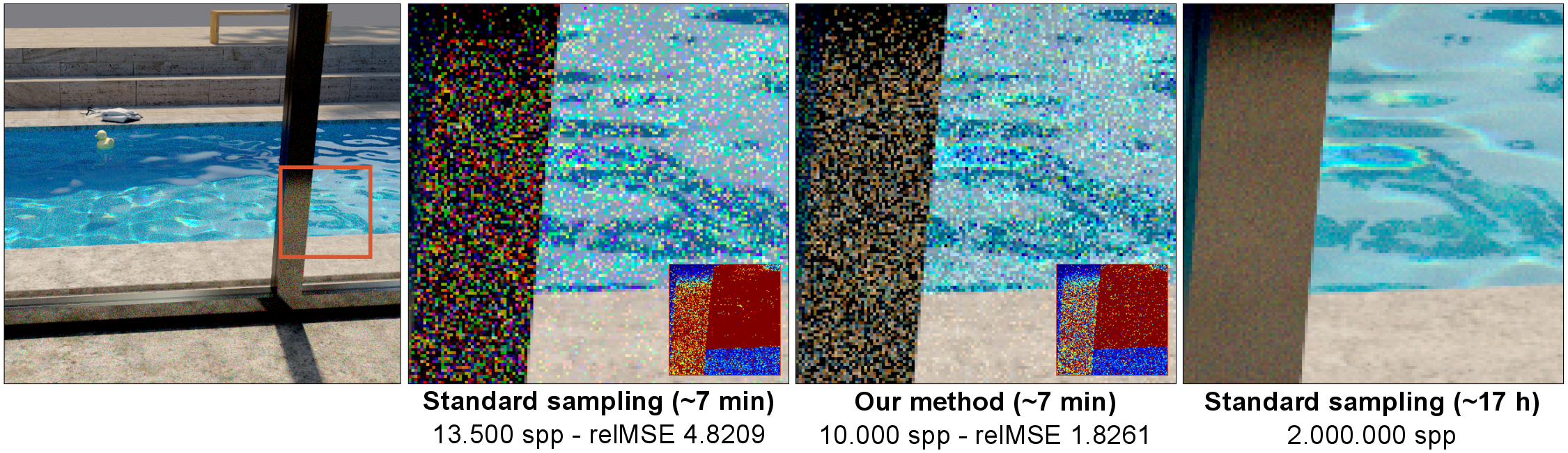
Spectral Monte-Carlo methods are currently the most powerful techniques for simulating light transport with wavelength-dependent phenomena (e.g., dispersion, colored particle scattering, or diffraction gratings). Compared to trichromatic rendering, sampling the spectral domain requires significantly more samples for noise-free images. Inspired by gradient-domain rendering, which estimates image gradients, we propose spectral gradient sampling to estimate the gradients of the spectral distribution inside a pixel. These gradients can be sampled with a significantly lower variance by carefully correlating the path samples of a pixel in the spectral domain, and we introduce a mapping function that shifts paths with wavelength-dependent interactions. We compute the result of each pixel by integrating the estimated gradients over the spectral domain using a one-dimensional screened Poisson reconstruction. Our method improves convergence and reduces chromatic noise from spectral sampling, as demonstrated by our implementation within a conventional path tracer.
Images and movies
BibTex references
@InProceedings { PBE18,
author = "Petitjean, Victor and Bauszat, Pablo and Eisemann, Elmar",
title = "Spectral Gradient Sampling for Path Tracing",
booktitle = "Computer Graphics Forum (Proceedings of EGSR)",
year = "2018",
url = "http://graphics.tudelft.nl/Publications-new/2018/PBE18"
}
![PBE18.pdf [10Mo]](/Publications-new/images/pdf.png)